On-Page SEO vs Off-Page SEO Complete Guide 2026

Search engine optimization (SEO) is no longer about tricks, shortcuts, or gaming Google. In today’s competitive digital landscape, SEO is about creating genuine value, building trust, and sending the right signals—both on your website and across the wider web.
At the heart of every successful SEO strategy are two fundamental pillars:
- On-page SEO – what you optimize on your website
- Off-page SEO – how the rest of the internet perceives your website
Many businesses struggle because they focus heavily on one and neglect the other. This guide goes deeper than surface-level definitions and shows you how on-page and off-page SEO actually work together to drive rankings, traffic, and conversions.
Whether you’re a business owner, SEO professional, blogger, or marketer, this article will give you a clear, actionable, and future-proof understanding of both concepts—written in simple, professional US English.
What Is SEO and Why It Matters More Than Ever
SEO is the process of optimizing your website so that search engines like Google can understand, trust, and rank your content for relevant search queries.
When done correctly, SEO helps you:
- Attract consistent, high-quality organic traffic
- Reduce dependence on paid advertising
- Build long-term brand authority
- Reach users at the exact moment they are searching
- Improve user experience and conversion rates
Unlike paid ads, SEO does not stop working the moment you stop spending money. However, it does require a strategic balance of on-page and off-page efforts.
Understanding the Difference: On-Page vs Off-Page SEO
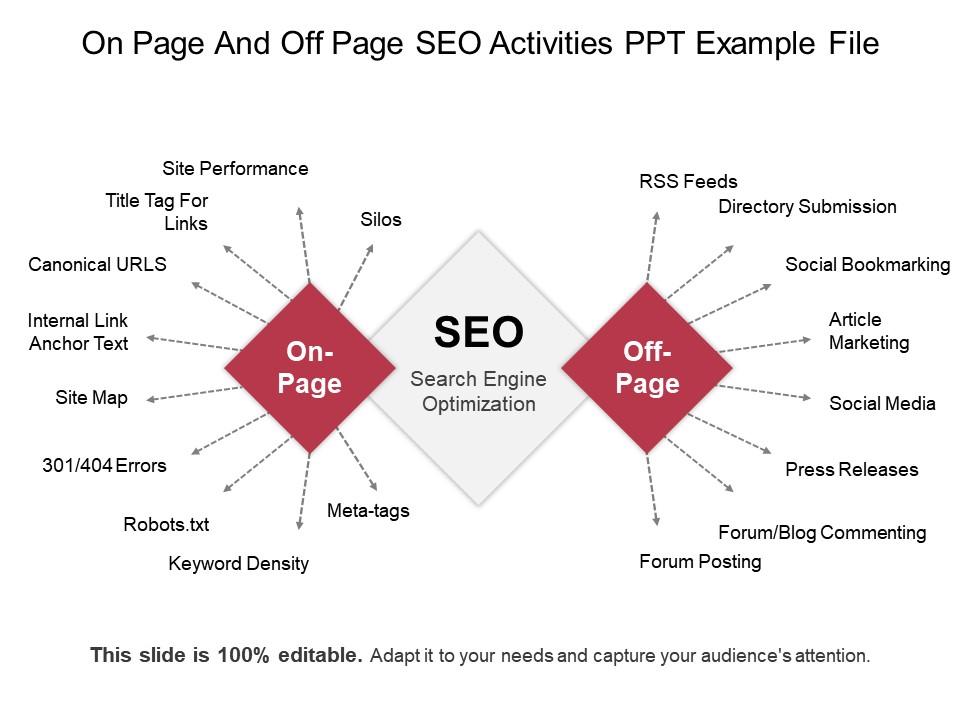
Before diving deep, let’s clarify the difference in the simplest way possible.
- On-page SEO focuses on optimizing your website’s content, structure, and technical elements.
- Off-page SEO focuses on building authority, trust, and credibility through external signals.
Think of your website as a store:
- On-page SEO is how clean, organized, and helpful your store is inside.
- Off-page SEO is what other people say about your store outside.
Both are essential. A great store with a bad reputation will struggle. A popular store with a messy interior will also fail.
What Is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to all optimization efforts you control directly on your website. Its main goal is to help search engines understand your content and help users consume it easily.
On-page SEO answers three critical questions for search engines:
- What is this page about?
- How useful is it for users?
- Is it structured and optimized correctly?
Core Elements of On-Page SEO
Let’s break down the most important components.
1. Keyword Research and Intent Matching
Every successful on-page SEO strategy starts with understanding search intent.
There are four main types of search intent:
- Informational (“what is on-page SEO”)
- Navigational (“Google Search Console login”)
- Commercial (“best SEO tools”)
- Transactional (“buy SEO services”)
Your content must match the intent behind the keyword. Ranking for a keyword is useless if your page does not satisfy what users actually want.
Best practices:
- Use one primary keyword per page
- Include related and semantic keywords naturally
- Avoid keyword stuffing
- Focus on clarity, not repetition
2. Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Title tags and meta descriptions are often the first interaction users have with your website in search results.
A strong title tag:
- Clearly explains the page topic
- Includes the primary keyword
- Stays under 60 characters
- Encourages clicks
A compelling meta description:
- Summarizes the page accurately
- Stays under 160 characters
- Uses persuasive language
- Improves click-through rate (CTR)
While meta descriptions are not a direct ranking factor, they strongly influence user behavior.
3. Headings (H1, H2, H3) and Content Structure
Proper heading structure improves both SEO and readability.
Best practices:
- Use one H1 per page
- Break content into logical sections using H2s and H3s
- Include keywords naturally in headings
- Make content scannable for users
Search engines use headings to understand content hierarchy, while users use them to find answers quickly.
4. High-Quality Content That Solves Problems
Content quality is the backbone of on-page SEO.
High-quality content should:
- Answer the user’s question completely
- Be accurate, original, and up to date
- Use simple, clear language
- Include examples, lists, and explanations
- Avoid fluff and unnecessary repetition
Longer content often performs better, but only when it delivers real value.
5. Internal Linking Strategy
Internal links help search engines crawl your website and distribute authority between pages.
Benefits of internal linking:
- Improves indexation
- Enhances user navigation
- Strengthens topical relevance
- Reduces bounce rate
Use descriptive anchor text and link only to relevant pages.
6. Image Optimization
Images improve engagement but can hurt performance if not optimized.
Image SEO best practices:
- Use descriptive file names
- Add keyword-rich alt text
- Compress images to reduce load time
- Use modern formats like WebP
Optimized images improve accessibility and page speed.
7. Page Speed and Core Web Vitals
Google prioritizes fast, user-friendly websites.
Key performance factors include:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- First Input Delay (FID)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Improving page speed reduces bounce rates and increases conversions.
8. Mobile Responsiveness
With mobile-first indexing, Google evaluates your site based on its mobile version.
Your site must:
- Adapt to all screen sizes
- Load quickly on mobile networks
- Offer smooth navigation
- Avoid intrusive pop-ups
9. URL Structure and SEO-Friendly Slugs
SEO-friendly URLs are:
- Short and descriptive
- Easy to read
- Keyword-focused
- Free from unnecessary parameters
Example:
- Good: /on-page-seo-guide
- Bad: /page?id=12345
10. Structured Data and Schema Markup
Schema markup helps search engines understand context.
Benefits include:
- Rich snippets
- FAQ results
- Higher CTR
- Improved visibility
While schema does not guarantee rankings, it enhances presentation.
What Is Off-Page SEO?
Off-page SEO refers to actions taken outside your website that influence how search engines evaluate your site’s authority, trustworthiness, and relevance.
While you cannot fully control off-page factors, you can strategically influence them.
Off-page SEO answers one critical question:
Can this website be trusted?
Key Off-Page SEO Factors
1. Backlinks: The Foundation of Authority
Backlinks are links from other websites pointing to yours.
Search engines treat backlinks as votes of confidence.
However, not all backlinks are equal.
High-quality backlinks:
- Come from authoritative websites
- Are contextually relevant
- Use natural anchor text
- Are earned, not manipulated
Low-quality or spammy links can harm your rankings.
2. Link Building vs Link Earning
Modern SEO focuses on earning links, not forcing them.
Effective strategies include:
- Publishing original research
- Creating in-depth guides
- Guest posting on relevant sites
- Digital PR campaigns
- Broken link building
The goal is to provide value worth linking to.
3. Brand Mentions (Linked and Unlinked)
Search engines recognize brand mentions—even without links.
Strong brand signals indicate:
- Authority
- Popularity
- Trust
Consistent brand mentions across reputable platforms improve off-page SEO.
4. Social Signals and Content Distribution
Social media does not directly impact rankings, but it amplifies reach.
Benefits include:
- Increased visibility
- More referral traffic
- Higher chances of earning backlinks
- Improved brand recognition
5. Online Reviews and Reputation Management
Reviews play a critical role in trust and local SEO.
Positive reviews:
- Increase conversions
- Improve local rankings
- Build credibility
Negative reviews, if handled professionally, can still build trust.
6. Local SEO and Citations
For local businesses, citations are essential.
A citation includes:
- Business name
- Address
- Phone number (NAP)
Consistency across directories strengthens local authority.
7. Influencer and Community Engagement
Being mentioned by industry leaders and participating in relevant communities helps build authority organically.
On-Page vs Off-Page SEO: A Strategic Comparison
| Aspect | On-Page SEO | Off-Page SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Location | On your website | Outside your website |
| Control | High | Partial |
| Focus | Content & UX | Authority & trust |
| Speed | Faster results | Long-term growth |
Which Is More Important?
Neither.
On-page SEO creates the foundation. Off-page SEO builds the reputation.
Without on-page SEO, off-page signals are wasted. Without off-page SEO, great content may never rank.
A Balanced SEO Strategy for Long-Term Success
To win in search:
- Start with strong technical and on-page SEO
- Publish valuable, intent-driven content
- Build authority through ethical off-page strategies
- Track performance and adapt continuously
SEO is not a one-time task—it is an ongoing process.
Final Thoughts
On-page and off-page SEO are not competitors—they are partners.
Websites that dominate search results are those that:
- Serve users better than anyone else
- Provide clear, structured, and helpful content
- Earn trust through authority and consistency
If you focus on long-term value instead of shortcuts, SEO becomes one of the most powerful growth channels available.